Waterways of Lake Godstone
Lake Godstone Waterways Development
Lake Godstone Waterways, situated approximately ten minutes north of Graford, Texas, represents a sophisticated blend of hydrological engineering, ecological management, and habitat enhancement, all developed with a focus on sustainable design.
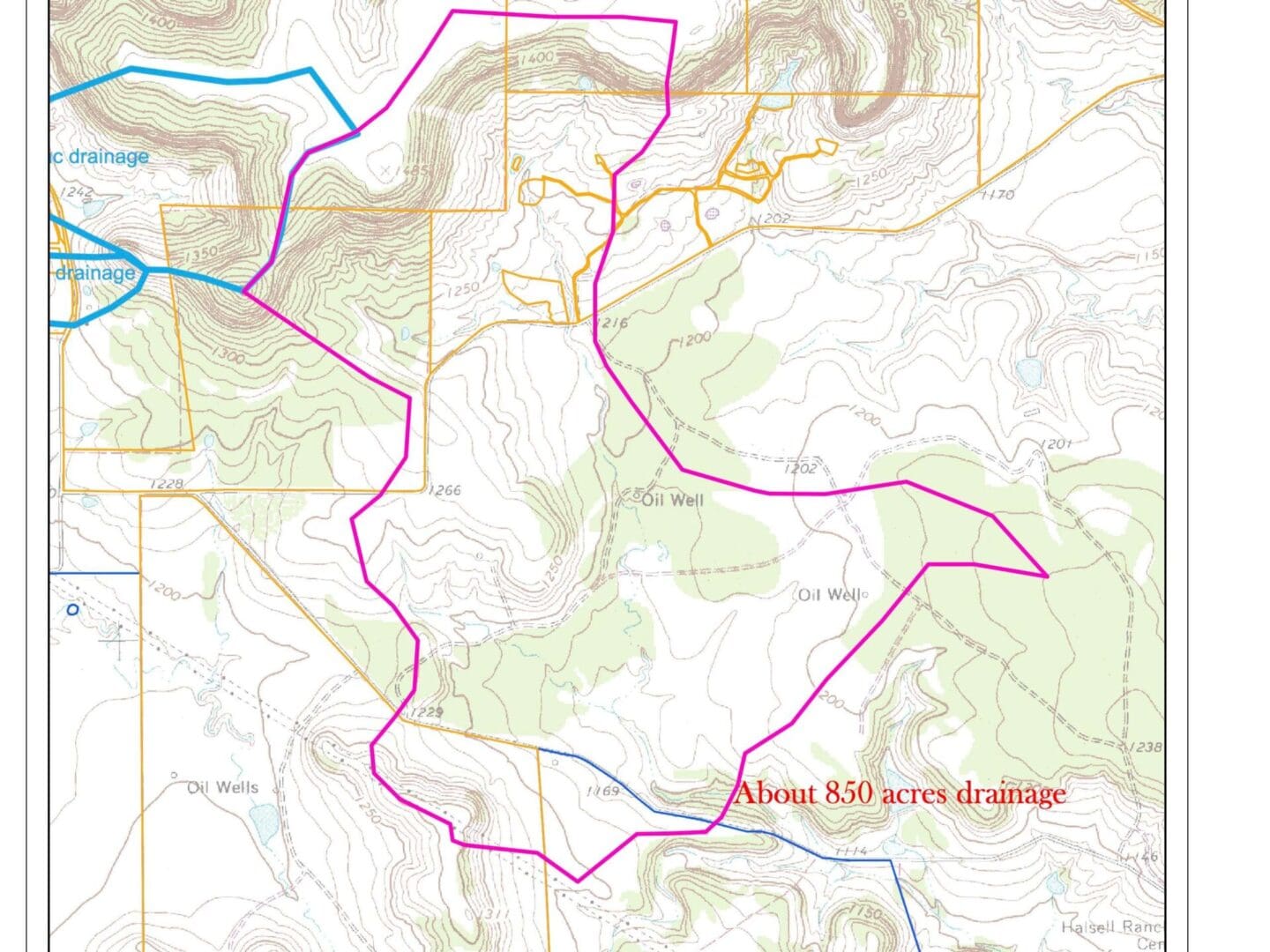
Construction of the lake began in July 2016, after clearance of the construction with the Texas Natural Resource Commission in Jacksboro (See drainage map provided by USDA NRSC below), Texas and transforming a previously undeveloped, heavily eroded landscape into a comprehensive recreational and ecological reserve.
Initial Construction and Geological Considerations
The creation of Lake Godstone Waterways required extensive excavation through complex geological strata. During initial construction, the dig site penetrated a 10-foot-wide limestone rock formation to a depth of approximately 15-20 feet. Below the limestone, the excavation continued into dense, nearly pure clay,with the final excavation layer reaching a 41-foot depth into blue shale clay. This specific combination of materials provided an ideal substrate for the lake’s bottom, ensuring stability and minimal seepage.
The lake’s primary dam structure, measuring 250 feet in length by 150 feet at the top, was formed from the excavated clay, with the dam slope built to a more gradual incline for increased stability. These slopes were engineered to reduce erosion and withstand hydrostatic pressure during heavy rain events.
Hydrological Engineering and Water Management Systems
A sophisticated water management system was developed to control the substantial watershed feeding into Lake Godstone Waterways. This system includes:
1. Spillways and Diversion Structures:•
Concrete Spillway: A critical feature constructed to handle overflow during extreme weather events. Originally installed in 2016, the spillway was later reinforced with concrete diversion walls and widened to manage increased runoff from the surrounding 850-acre watershed.
Trickle Tubes: The dam was equipped with multiple trickle tubes to regulate groundwater flow. A 24-inch trickle tube directs water away from the lake during moderate rainfalls, while two 48-inch tubes manage overflow from the Crappie Pond, preventing uncontrolled flooding into the downstream ecosystems.
2. Retention and Distribution Ponds:
• To mitigate the impact of large-scale runoff and facilitate groundwater recharge, a network of twelve retention ponds was developed. These ponds temporarily collect stormwater, promoting infiltration into deeper limestone aquifers and supplying a consistent water source to local vegetation and wildlife during dry periods.
3. Pumping and Irrigation Infrastructure:
• A robust pump system was installed to maintain water levels across interconnected ponds, notably the Catfish Pond. This system includes a 2-inch pipeline that extends approximately 400 feet, transferring water from Lake Godstone Waterways to the Catfish Pond, thereby sustaining the aquatic environment during droughts and creating a one-acre wetlands between the Catfish Pond and the Beaver Pond.• The irrigation setup also supports the Monarch Butterfly Station, minnow and frog pond, birdbath station, sports fields, and a children’s playground area, ensuring the vitality of plant life and maintaining green spaces across the property.
• To establish water sources at wildlife feeding stations, a dedicated water well was drilled at the northern boundary of the property, with an additional well installed at the eastern extremity. A subterranean water pipeline extending approximately 0.5 miles was constructed from the northern well to the primary water well located at the maintenance shed, forming a redundant water supply system to enhance operational resilience. Both water wells were subsequently integrated into the infrastructure of the newly developed cabins and campgrounds in their respective vicinities, ensuring a reliable supply of water to these facilities.
• The lake water pump system was interfaced with a dedicated water distribution line designed to deliver water to a small, controlled minnow pond and an adjacent birdbath positioned near the bird observation facility. This system is engineered to facilitate continuous water circulation, with overflow from the minnow pond channeled back to the lake via a structured concrete spillway, ensuring efficient water management and ecosystem sustainability.
• The aquaponics greenhouse situated behind the lodge is supplied with water sourced directly from the lake. During the spring and fall seasons, Bluegill are introduced into the greenhouse’s water reservoir, where they contribute essential nutrients to support theaquaponic vegetable cultivation system. This closed-loop setup serves as a practical demonstration to educate guests on the principles of ecosystem dynamics and nutrient cycling in natural environments.
Aquatic and Wetland Habitat Development
Lake Godstone Waterways ecological strategy included the enhancement of its aquatic and wetland environments to support a diverse array of species:
• Spawning Ledges: Three pea gravel spawning ledges, each 12 feet wide and situated at a depth of approximately 10 feet (when the lake is at full capacity), were constructed along the lake’s perimeter. These ledges provide optimal conditions for fish reproduction, particularly for species such as largemouth bass, bluegill, and crappie.
• Catfish Pond Rehabilitation: Initially prone to seasonal desiccation, the Catfish Pond’s water stability was vastly improved by the direct water transfer system from Lake Godstone Waterways. This intervention included the installation of a 300-pound fish feeder and the introduction of species like Red Swamp crayfish, channel catfish, and bluegill to establish a balanced aquatic ecosystem in the ponds and the wetlands.
• Crappie Pond Dynamics: Built in 2020, the Crappie Pond is maintained at a consistent 12-foot depth, supported by both surface runoff and sub-surface springs originating from Lake Godstone™. The pond’s design incorporates half of its area into a wooded zone, providing natural cover for fish species and creating a microhabitat that supports both aquatic life and terrestrial wildlife
.• Feral Hog Elimination: A perimeter feral hog-proof fence was constructed around the 188-acre reserve to safeguard the Bee Hives, watering holes, wetlands and other wildlife habitats from extensive damage caused by feral hogs. This fence undergoes regular inspections and maintenance to ensure its effectiveness and longevity. barbed wire was eliminated from the hog fencing to permit safer deer crossings to and from our property over the four-foot fencing.
• Bees, Butterflies and Vegetation: Rainwater provides water for our lake and ponds at Lake Godstone™ and pollinators are attracted to the land due to growing fields of flowering vegetation of all types. Our Green Antelope Milkweed fields are thriving and thanks to regular introduction of native perennial and annual flowers over the years the landscape is expanding quickly to support our Bee Hives and Monarch Butterly Waystation.
• Bats, Bluebirds, Ducks and Owls: Nesting boxes have been strategically installed throughout the 188-acre campus to attract and support wildlife by providing habitat close to essential water sources. Specific attention has been given to the placement of bat boxes, as bats are particularly drawn to environments with lakes, ponds, and surrounding vegetation. Proper positioning of these bat boxes is crucial to ensure they effectively attract and accommodate bat populations.
Lake Aeration and Ecological Management
The lake’s depth, reaching up to 40 feet, presents a risk of stratification and oxygen depletion, which could lead to fish die- offs during seasonal turnovers. To prevent this, a lake aeration system was implemented in 2023, continuously infusing thedeepest areas of the lake with oxygen. This system plays a crucial role in maintaining water quality and supporting a stable fish population.
Additionally, recommendations from wildlife biologists led to the installation of six fish feeders around Lake Godstone™ to promote healthy growth rates for game fish species. Enhanced brush cover was also introduced to the lake’s perimeter, offering shelter and breeding grounds for both fish and invertebrates.
Wildlife and Vegetation Management
Lake Godstone’s 188-acre campus includes a diverse array of habitats designed to support both local wildlife and migrating species:
• Feed and Water Stations: Strategically placed throughout the property, these stations serve the needs of local fauna, including deer, raccoons, coyotes, bobcats, and a range of bird species like herons, scissor-tailed flycatchers, painted buntings, and red-winged blackbirds. Each station is equipped with reliable water sources fed by on-site wells and designed to be accessible year-round.
• Butterfly and Pollinator Gardens: Forty butterfly bushes have been planted near the Monarch Butterfly Station to attract and sustain pollinators, supported by the irrigation system derived from the lake’s water supply. These gardens not only enhance the visual appeal of the area but also contribute to the conservation of essential pollinator species.
Infrastructure for Visitor Engagement and SustainabilityThe design of Lake Godstone’s facilities focuses on blending functionality with minimal ecological impact:
• Non-Motorized Watercraft Policy: Only non-motorized boats are permitted on Lake Godstone™, reducing potential water pollution and protecting the tranquility of the wildlife habitat. Available rentals include kayaks, canoes, pedal boats, and a rowboat, along with an eight-person pontoon boat with a trolling motor.
• Lodge and Campground Connectivity: The entire campus is interlinked by six miles of all-weather gravel roads, with specific areas designed for accessibility and outdoor recreational use. Each lodging unit, including the lodge, guest homes, cabins, and campgrounds, is equipped with power, water, picnic facilities, and spacious fire pits for group activities.
Conservation Practices and Sustainability Initiatives
Lake Godstone’s commitment to conservation is reflected in every aspect of its design and operations:
• Rainwater Harvesting and Watershed Management: The infrastructure capitalizes on the natural watershed from surrounding areas to maintain lake levels and replenish water bodies, even during prolonged droughts. The retention ponds and spillways are critical to mitigating erosion and managing peak water flows efficiently.
• Lake Godstone™ Apiary and Flora: A small apiary on the property supports local pollinators, while seasonal flowers and native vegetation contribute to the area’s biodiversity. These features not only enhance the natural beauty but also play a key role in supporting the local ecosystem.Please visit our reviews and book your next family adventure today.”
Call 940-275-0908 to book your retreat nowWe invite you to book your stay at Lake Godstone, where unforgettable memories await you in a tranquil, wildlife-rich environment. Don’t miss the chance to connect with your loved ones amid stunning landscapes. Visit www.LakeGodstone.com to discover more about our offerings and plan your adventure today!